The tooth fairy is a welcome guest for any child who has lost a tooth. Not only will the fairy leave a small gift under the child’s pillow, but they be assured of a replacement tooth in a few months. Unfortunately, the scenario is quite different for adults grappling with a loss of teeth. Luckily, there may be some hope thanks to a new study performed by scientists at Kyoto University and the University of Fukui.
A dental breakthrough
While the typical adult mouth houses 32 teeth, approximately 1% of the population exhibits variations of them, either possessing more or fewer teeth due to congenital conditions. Researchers have delved into the genetic factors behind cases of excessive teeth, seeking valuable insights into the potential regeneration of teeth in adults. This study is the first to show that monoclonal antibodies can help regrow teeth. It suggests a new way to treat a dental problem that currently requires implants and other artificial solutions.
A bit of science
The research team disclosed that an antibody targeting a specific gene, known as uterine sensitization-associated gene-1 (USAG-1), can induce tooth development in mice affected by tooth agenesis, a congenital condition. The findings were published in the journal, Science Advances.
As per Katsu Takahashi, a senior lecturer at the Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine and one of the principal contributors to the study, the essential molecules crucial for the development of teeth have already been pinpointed. “The morphogenesis of individual teeth depends on the interactions of several molecules including BMP, or bone morphogenetic protein, and Wnt signaling,” says Takahashi.
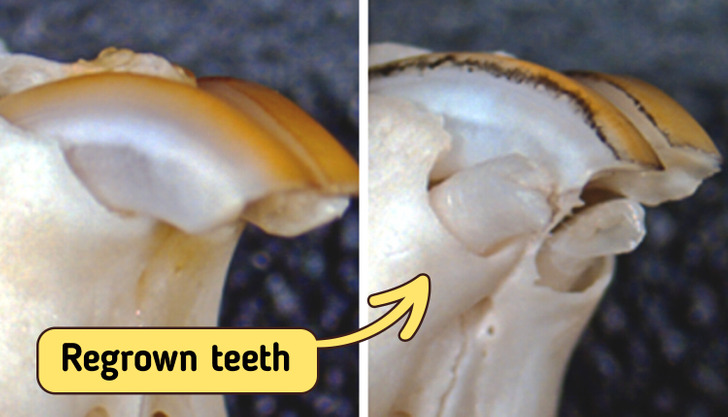
On April 13, 2021, the University of Kyoto posted its first pic of newly-grown teeth in mice.
BMP and Wnt are involved in more than just tooth development; they affect the growth of organs and tissues early in the body’s development. Because drugs affecting them directly might have broad side effects, scientists are cautious. To find a potentially safer method, researchers focused on the gene USAG-1, thinking that aiming at factors countering BMP and Wnt specifically in tooth development could be more precise.
“We knew that suppressing USAG-1 benefits tooth growth. What we did not know was whether it would be enough,” added Takahashi.
The first results
Scientists looked at how different monoclonal antibodies affect USAG-1. Monoclonal antibodies are often used to treat things like cancer and arthritis and for making vaccines. Tests with this antibody showed that BMP signaling is crucial for deciding the number of teeth in mice. Also, just one treatment was enough to grow a whole tooth. Further tests confirmed these positive results in ferrets too.
“Ferrets are diphyodont animals with similar dental patterns to humans. Our next plan is to test the antibodies on other animals, such as pigs and dogs,” explained Takahashi.
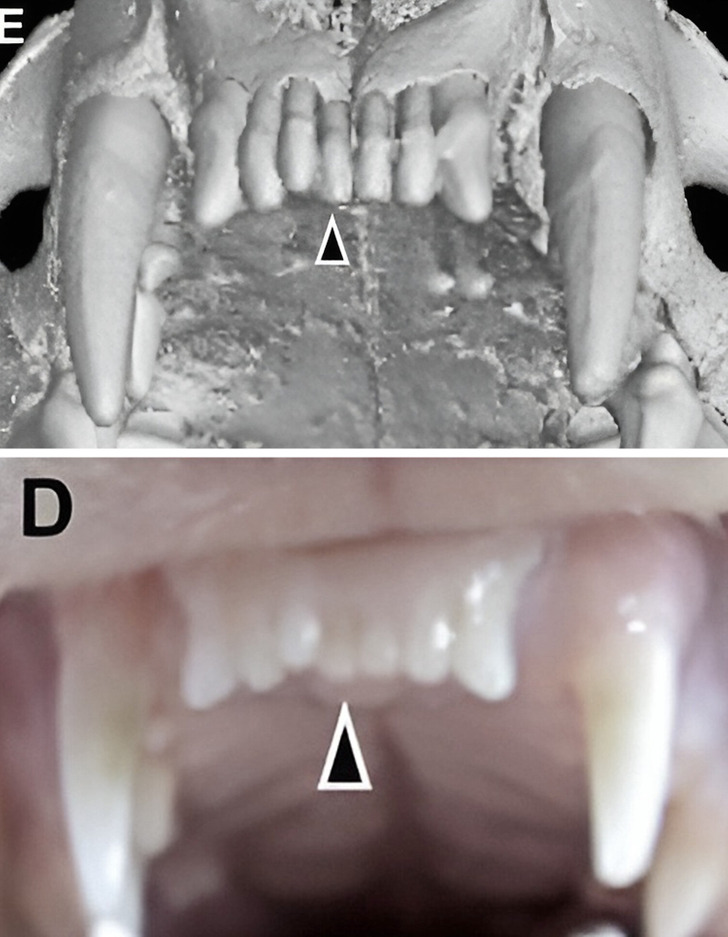
Fully regrown frontal teeth in ferrets
The next steps

Now, scientists are going to test the drug on healthy adults. If that goes well, the team plans to try it on kids aged 2 to 6 with a rare tooth problem called anodontia, a genetic disorder defined as the absence of all teeth. These kids will get one shot of the drug to see if it makes their teeth grow. If everything works out, the medicine might be approved by 2030.
Takahashi sees the new medicine as an additional choice for individuals who are missing some or all of their teeth.
“The idea of growing new teeth is every dentist’s dream,” Takahashi told the Japanese newspaper, The Mainichi in June this year. “I’ve been working on this since I was a graduate student. I was confident I’d be able to make it happen.”
So hopefully, by the year 2030, humans will get a chance to have their third generation of teeth grown and say goodbye to implants. Until then, make sure to keep your teeth strong and healthy — this article will help you with that.
Preview photo credit KyotoU_News / Twitter
I Accidentally Saw My Husband in a Shop Line & Got a Text from Him the Next Moment – My World Shattered

Jessica planned a special surprise for their 10th anniversary, but a shock awaited her at the local store. What she mistook for betrayal turned into an unforgettable celebration of love and trust.
Today marks ten years—ten whole years since George and I said “I do.” With each anniversary, I try to make things special, but this year, I wanted it to be unforgettable. So, I planned a surprise with all of George’s favorite things, the ones he doesn’t treat himself to often.

Woman in a grocery store | Source: Pexels
There’s this little gourmet shop downtown that sells the best artisanal cheeses and craft beers, George’s favorites. He’d never spend money on them himself, but I knew they would make his day.
The shop was bustling, a typical scene for a Saturday morning. I navigated through the aisles, my basket slowly filling up with treats. The air was rich with the smell of freshly baked bread and coffee. It felt good to be doing something special for him, thinking about his smile when he’d see what I got him.

Grocery store | Source: Pexels
As I waited in line to pay, the hum of voices around me blended into a familiar sound. A voice I knew better than my own. George’s voice. My heart skipped. He was supposed to be across town, stuck in traffic. That’s what he texted just ten minutes ago. Confused, I peeked around the person in front of me.
There he was, not a hint of traffic stress on his face. And he wasn’t alone. He was with my mom, laughing about something on his phone, her hand lightly touching his arm.

Man in a grocery store | Source: Pexels
My stomach churned. Why would he lie? Why was he here with her, looking so… happy? The line moved, but I was frozen, a mix of disbelief and dread washing over me.
My phone buzzed in my pocket, pulling me back from the shock. Another message from George: “Really stuck here, babe. Might take even longer. Love you.”
The words blurred before my eyes. Love you? Did he really? My hands shook as I typed a quick reply to say I understood, while a storm of doubt raged inside me.
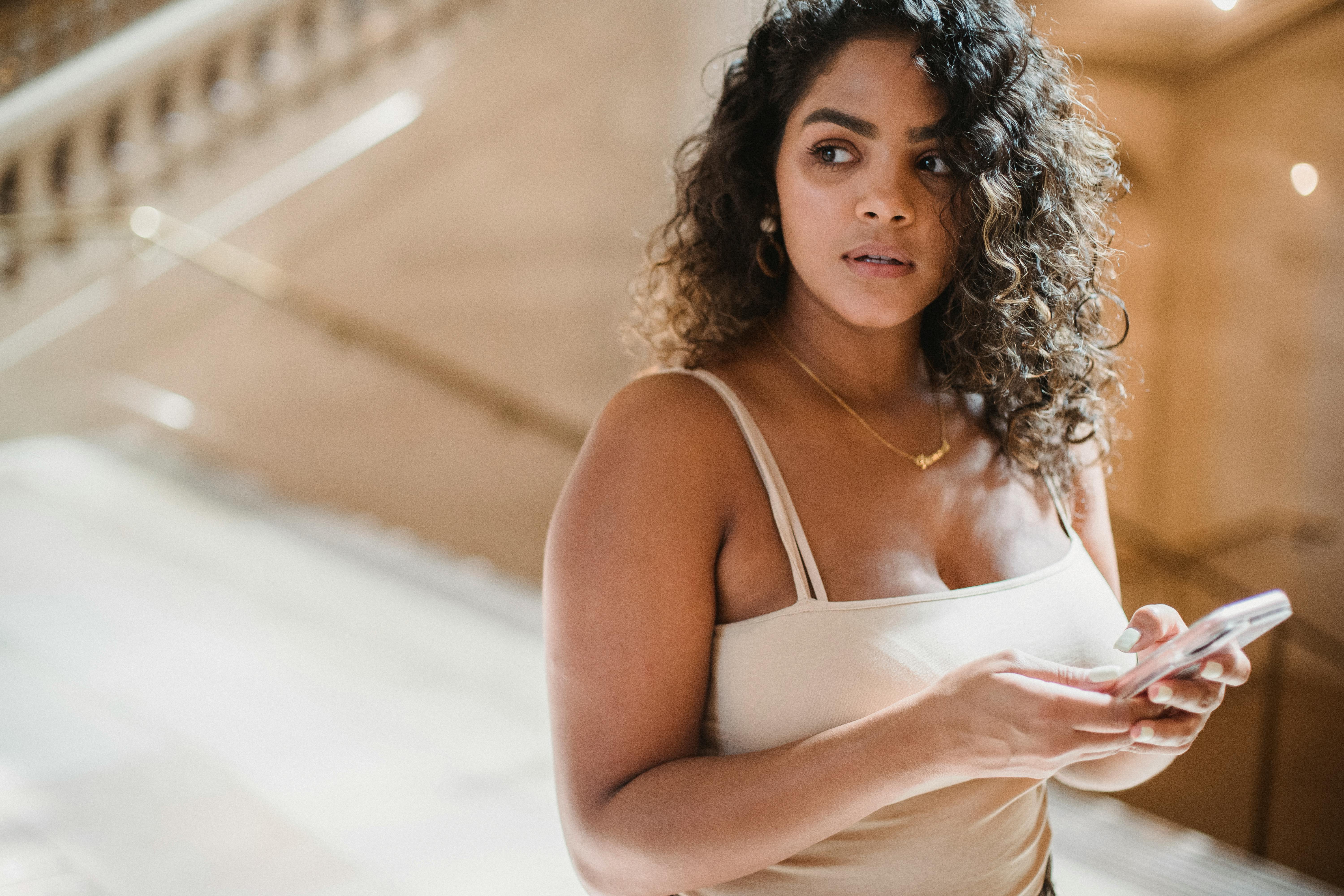

Suspicious woman on her phone | Source: Pexels
I couldn’t just confront them—not there, not with so many eyes watching. I needed answers, and the only way to get them was to follow them discreetly.
So, I hung back, my shopping forgotten, as they left the store together. They seemed so at ease with each other, too comfortable. My mind raced with every step they took—had there been signs I missed?
I followed them at a distance, my heart pounding in my ears. They didn’t notice me. They walked down the streets like any pair might on a sunny morning, occasionally laughing, completely absorbed in their own little world. That hurt the most, seeing them like that.
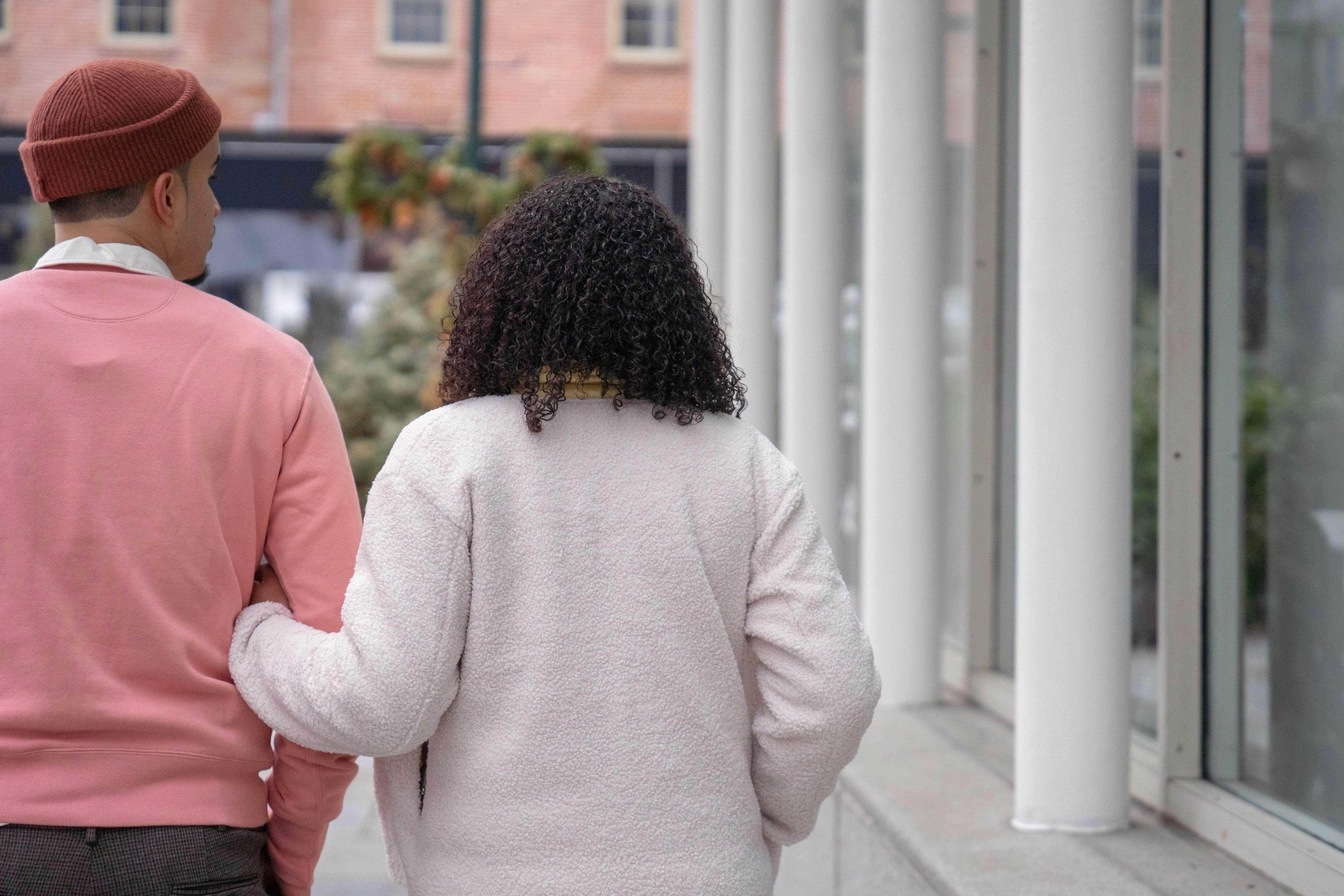

Man and woman walk on the street | Source: Pexels
As they turned into my mom’s street, a million scenarios ran through my head. Each was worse than the last. What would I do if my worst fears were confirmed?
Could I forgive either of them? I parked my car a little way down from her house and waited, watching them enter with ease, like it was the most natural thing in the world.
Sitting there, in the driver’s seat, I felt a sense of betrayal so deep it was hard to breathe. My mom, my confidante, and George, the love of my life—how could they do this to me?
I wiped away tears that stung bitterly, knowing I had to face whatever was happening inside. With a deep, shaky breath, I steeled myself to walk up to the door. I had to know the truth, no matter how much it would hurt.

Jessica follows her mother and husband | Source: Midjourney
I stood in front of my mom’s house, my heart thumping so loud I could barely hear the birds chirping in the suburban quiet. It took every ounce of courage I had to step up to the door, my hand trembling as I reached for the handle. The door swung open before I even touched it, and what I saw inside stopped me in my tracks.
The living room was transformed. Twinkling lights were strung across the ceiling, casting a soft, warm glow over dozens of flowers and balloons that filled the space. There was a table set for two, with candles and a dinner that looked almost ready to be served. Banners saying “Happy 10th Anniversary!” hung on the walls. It was beautiful, surreal.
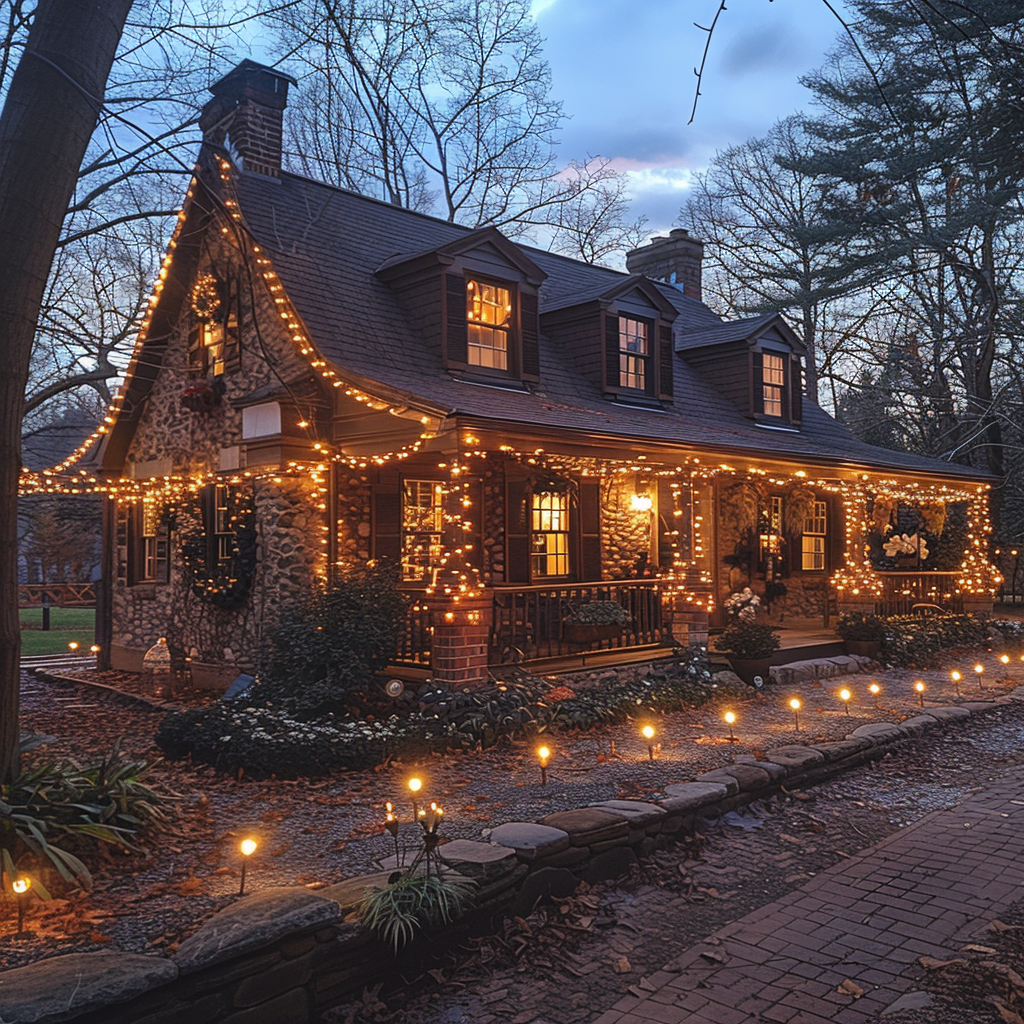

The house | Source: Midjourney
George stood there, a nervous smile playing on his lips. My mom was beside him, her eyes sparkling with excitement and maybe a hint of guilt. “Surprise!” they said in unison, but all I could do was gape at them, the anger draining out of me as confusion set in.
“But… the text? You said you were stuck in traffic,” I managed to stammer out, my voice shaky.
George stepped forward, his expression tender. “I’m sorry for the text, Jess. I just needed a bit more time to get everything ready here. I wanted it to be perfect.” He gestured around at the decorated room.

Jessica’s mother | Source: Midjourney
“And I had to keep you away somehow,” Mom chimed in, coming to hug me. “We wanted to surprise you, sweetheart. We’ve been planning this for months!”
As the initial shock wore off, relief washed over me, mingling with a warmth that spread through my chest. I looked between the two of them, seeing only genuine love and excitement in their faces. The secrecy, the lies—it was all for a surprise that they hoped would make me happy.
George wrapped his arms around me. “I love you so much, Jess. I wanted to celebrate our ten years together in a special way. I couldn’t have pulled this off without your mom.”
The house party | Source: Pexels
The tension I hadn’t even realized I was holding began to melt away. I hugged them both, laughter bubbling up from somewhere deep inside me. “You guys… I thought—never mind what I thought. This is incredible.”
We spent the next few hours talking, laughing, and sharing stories. Mom recounted how they sneaked around to organize the surprise, and George apologized for any worry he caused. It felt like a renewal, a reminder of the strong bonds we shared.

Man and woman dancing | Source: Pexels
As the evening settled in, George took my hand and led me to the center of the room. Music began to play, a soft melody that had always been special to us. We danced slowly, our bodies close, and I felt every bit of tension melt away. With each step, each turn, I could feel our trust and connection rebuilding, stronger than before.
“I thought I lost you today,” I whispered, my head against his chest.
“You’ll never lose me,” he replied, his voice steady and sure. “I’m sorry for the scare, Jess. Let’s promise to keep the lines open, always, no matter what.”

Woman laughing with her friends | Source: Pexels
I nodded, my heart full. Today had taught me more than I could have imagined about trust and communication. It wasn’t just about not keeping secrets; it was about being there, truly and completely, for each other.
The surprise George and my mom planned was intricate and beautiful, crafted with so much love and care. I knew I would cherish this memory forever, not just because of the celebration itself but because of what it represented. I was loved, deeply, and that was worth every confusing, heart-stopping moment of today.

Woman hangs out with her friends | Source: Pexels
Later, as I recounted the day’s adventures to a group of friends, laughter and awe filled the air. My story of misunderstandings turned into magical joy became a favorite, a reminder of how unexpected turns can lead to the most beautiful destinations. It reinforced a simple, profound truth: love and trust, even when tested, can bring the sweetest surprises.
This work is inspired by real events and people, but it has been fictionalized for creative purposes. Names, characters, and details have been changed to protect privacy and enhance the narrative. Any resemblance to actual persons, living or dead, or actual events is purely coincidental and not intended by the author.
The author and publisher make no claims to the accuracy of events or the portrayal of characters and are not liable for any misinterpretation. This story is provided “as is,” and any opinions expressed are those of the characters and do not reflect the views of the author or publisher.



Leave a Reply