
Ever ponder how much it truly costs to maintain a Tesla for an entire year? Given the initial expensive cost of Tesla vehicles, one may think that recurring electrical costs would be exorbitant. Surprisingly, though, that is untrue.
After driving a Tesla for a year, someone recently revealed their electricity bill on social media, and it was surprisingly low. The photo was humorously captioned, “First bill in 12 months. ‘This sucks.’” What is the approximate annual amount of their electricity bill? Merely $2.37 (£1.89)!
Perhaps you’re asking yourself, “How is that even possible?” Now, for the reveal. A Tesla Powerwall, a potent battery that is connected to the home’s electrical supply, was part of the individual’s setup. In the event that solar panels are installed, this technique is quite advantageous. The Powerwall is charged by the excess solar energy, and the car is powered by it.
There’s a catch, though. The cost of the Tesla Powerwall is quite high, ranging from $11,500 (£9,000) to $15,000 (£11,800). Even though this cost might appear high up front, for people who intend to retain their Tesla for a long time, it might end up being economical. However, it’s important to remember that not everyone has the resources to make this kind of commitment.
We cannot dispute the fact that the initial setup costs a substantial amount of money, even with a Tesla’s generally low electricity bills. Thus, before selecting a choice, it’s critical to take your personal financial circumstances and long-term goals into account.
Ultimately, it’s crucial to thoroughly consider the advantages and disadvantages of having a Tesla, even though some individuals may be surprised by the electricity bills. Furthermore, one can never predict what novelties Tesla may discover down the road. The Cybertruck, their most recent invention, is already causing a stir. So, if a Tesla is something you’re thinking about, stay tuned for future developments!
Katy Perry has once again captured the spotlight with her unapologetic style.
The pop icon, known for her daring fashion sense, arrived at an award event in a stunning getup that raised some eyebrows.
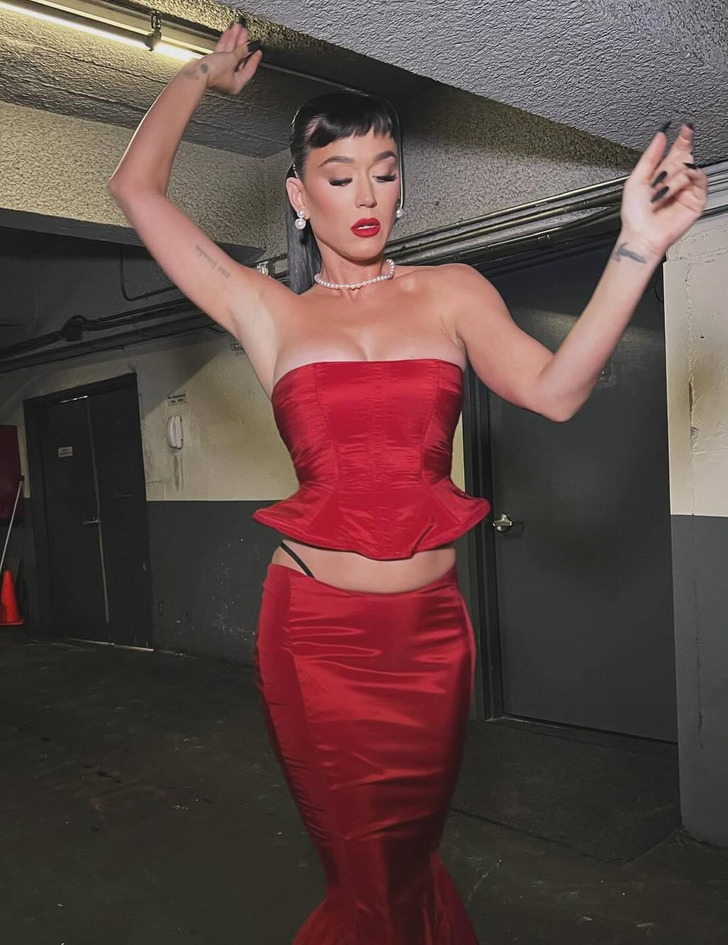

Katy Perry’s latest look was a showstopper with a bold black thong visible under a vibrant red skirt that laced up. She paired it with a corset top and towering black heels, radiating sheer confidence. Her sleek ponytail was the perfect match for her pearl necklace and earrings.
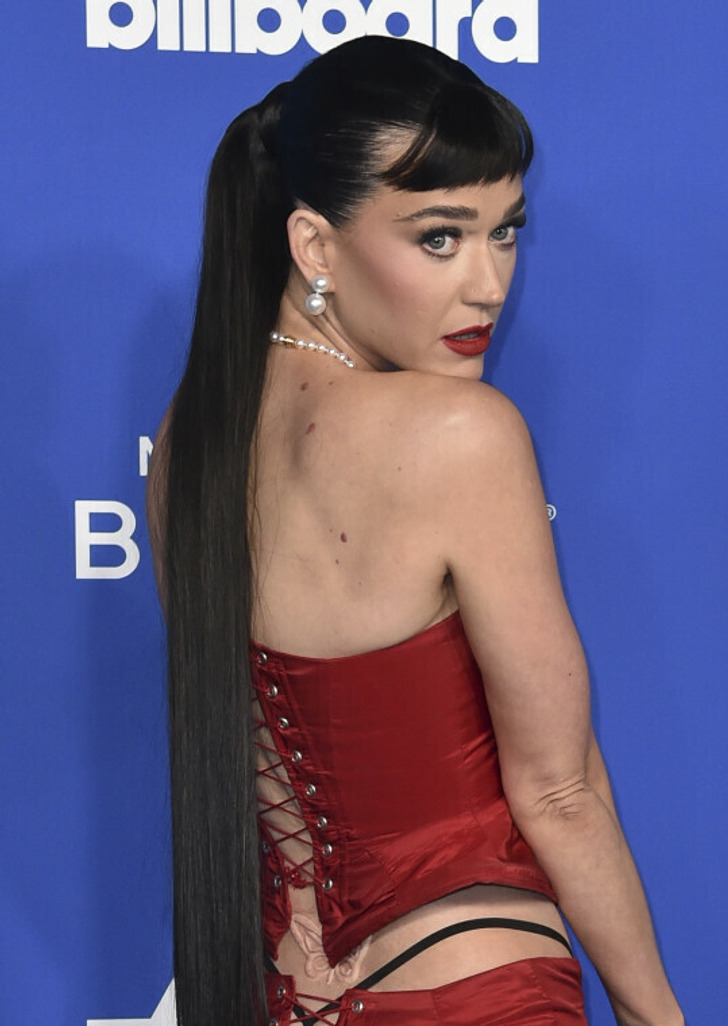

But it wasn’t just her clothes that made waves; Perry also showed off a new 3D skin color prosthetic tattoo of a butterfly on her lower back.
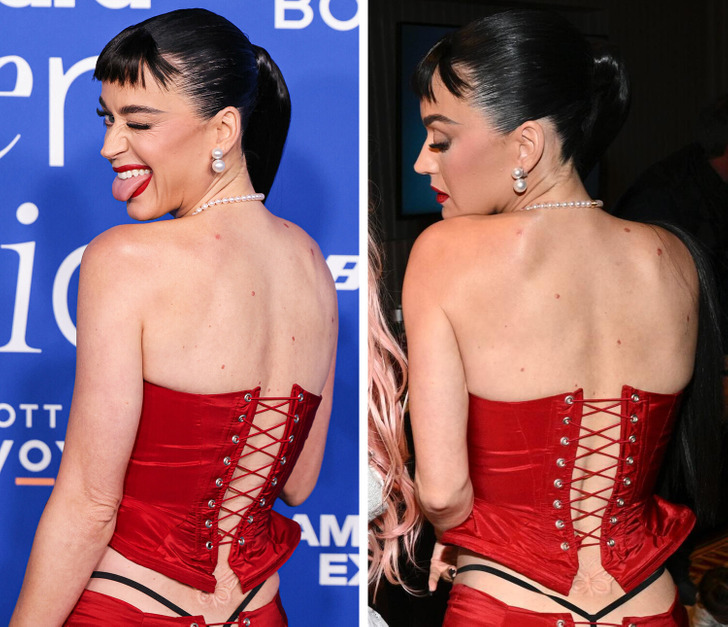
Katy’s bold look and the tattoo earned her praise from the fans but some also expressed their unhappiness. «I’m sad that children see this….» commented a person on Katy’s photo. «Sorry but this dress and butterfly tattoo or whatever it is is ew,» added another.

Another celebrity who made headlines for their risky outfit is Kristen Stewart who opted for a look without pants. Check out her photos here.
Preview photo credit Richard Shotwell/Invision/East News, katyperry / Instagram



Leave a Reply