Ever wondered just how much data your brain can hold? We often compare the brain to a supercomputer, but what if that comparison isn’t just a metaphor—it’s literal? Deep within your brain, at the junctions where neurons meet, lies an extraordinary form of biological storage: the synapse. And thanks to breakthroughs in information theory, we’re beginning to quantify its staggering capacity.
In this article, we’ll dive into how synaptic storage works, how scientists measure it, and why this knowledge could shape the future of data storage—from artificial intelligence to DNA-based memory.
What Are Synapses and Why Are They Important?
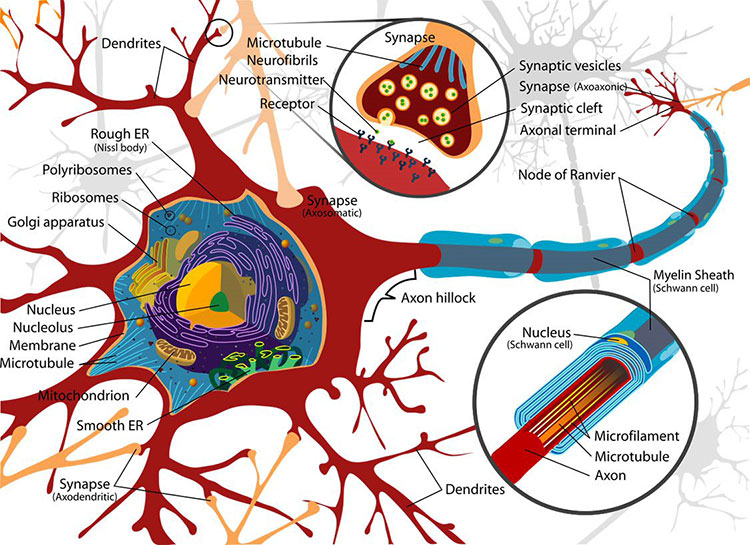
Think of neurons as the brain’s messengers. But without synapses—the gaps between them where signals are transmitted—those messages would go nowhere. A synapse is where the magic happens: it’s the space where one neuron sends a chemical or electrical signal to another, sparking thoughts, memories, movements, and more.
Now here’s the kicker: each of these tiny junctions doesn’t just pass along data—it stores it.
Your brain has about 86 billion neurons, and each one can form around 1,000 synapses. That’s a total of roughly 125 trillion synapses buzzing away in your brain, constantly sending and receiving signals. These connections form the foundation of your memories, knowledge, and perception.
Measuring Synaptic Storage with Information Theory
To understand how synapses store information, scientists turn to information theory—a branch of mathematics that deals with encoding, decoding, and compressing data. Think of it like analyzing how much a hard drive can hold, but on a biological scale.
Video : 2-Minute Neuroscience: Synaptic Transmission
Each synapse, as it turns out, can store up to 4.7 bits of information. That might not sound like much until you consider the scale:
- 1 bit is a single piece of binary data (a 0 or 1)
- 4.7 bits per synapse × 125 trillion synapses = over 500 trillion bits of potential storage
Translated into digital terms, your brain can theoretically store more data than the entire internet—all in a compact, low-energy package powered by biology.
The Brain’s Efficiency: Powering Trillions of Connections
Here’s something even more mind-blowing: while your laptop heats up and guzzles electricity, your brain handles all of this complex storage and processing using roughly 20 watts of power—that’s about the same as a dim light bulb.
This insane efficiency is what’s inspiring researchers to build neural networks and deep learning systems that mimic the brain. If computers could process and store data like synapses do, we’d have faster, smarter, and greener technology.
Artificial Intelligence and Synaptic Models
The field of AI, especially machine learning and deep learning, borrows heavily from how the brain processes and stores information. Artificial neural networks use layers of interconnected nodes (inspired by neurons) to simulate learning.
But here’s where it gets interesting: researchers are now using real data about synaptic information capacity to refine these systems. The goal? To build AI models that are more human-like, not just in intelligence but in efficiency and adaptability.
Imagine a future where your smartphone thinks and stores information with the same elegance as your brain. That future isn’t science fiction—it’s science.
Beyond the Brain: DNA as the Ultimate Storage Device
While the brain remains the pinnacle of biological storage, it’s not the only game in town. Enter DNA, nature’s original information vault.
DNA doesn’t just code for life—it can be used to store digital data. And we’re not talking small files here. A single gram of DNA can hold up to 215 petabytes of data. That’s 215 million gigabytes—enough to store every photo, song, and document you’ve ever owned, plus millions more.
In fact, researchers have already done it. In one groundbreaking study, scientists encoded a 52,000-word book into synthetic DNA. They converted the digital content into binary (0s and 1s), then translated those digits into DNA’s four-letter alphabet: A, T, G, and C. The result? A physical strand of DNA holding a complete, retrievable digital file.
Why DNA Storage Matters for the Future
Traditional storage devices—hard drives, SSDs, even cloud servers—have physical limits. They degrade over time and take up massive amounts of space. DNA, on the other hand, is incredibly compact, durable, and stable for thousands of years if stored properly.
If scaled correctly, DNA storage could revolutionize how we preserve knowledge. Imagine backing up the entire contents of the Library of Congress on something no bigger than a sugar cube. That’s the level we’re talking about.
Video : How Your Brain Remembers: Neurons & Synapses Explained!
Bridging Biology and Technology
What’s exciting is how these two areas—brain synapses and DNA storage—are starting to intersect. Both are nature’s proof that small-scale systems can handle mind-blowing amounts of data. As scientists continue to decode these systems using information theory, they’re finding ways to integrate them into technology.
It’s not about replacing computers with brains or turning DNA into a USB drive. It’s about learning from nature’s most efficient designs to build the next generation of computing and storage systems.
Conclusion: Reimagining Storage in a Biological World
Your brain’s 125 trillion synapses silently store and process more information than entire server farms, all while sipping on 20 watts of energy. Meanwhile, DNA—the code of life—is showing us how to pack massive libraries of data into microscopic strands.
By measuring synaptic storage capacity with information theory, we’re not just understanding the brain better—we’re laying the foundation for a new era of intelligent, efficient technology.
The takeaway? Nature has already solved problems we’re only beginning to understand. And the more we study it, the closer we get to unlocking the true potential of both our minds and our machines.
Weeks Before the Wedding, Woman Discovers Disturbing Secrets About Her Future Husband

A woman has recounted the devastating story of how she discovered her fiancé had been lying about his entire life just weeks before their wedding.
Most of us are guilty of telling the odd white lie when dating, but how far would you go in order to impress a potential significant other?
For Megan Clarke, 27, she thought she’d found her happy ever after when she begun a relationship with Lord Bertie Underwood, a charming horologist (someone who makes and repairs watches).
Although she wasn’t looking to settle down, Megan – who was 20 years old at the time and working as a bar manager on the Isle of Wright – was soon swept off her feet by the dashing Lord, who treated her to luxurious date nights and invited her to live in his lavish seafront home.
“He was charming, kind, thoughtful, loving. A real gentleman,” Megan recounted of their relationship during an interview with Metro.
The relationship moved quickly. Within a month the pair had said ‘I love you’ and Bertie would pop the question six months later, surprising Megan with a Cartier diamond ring.
However if things sound almost too good to be true, there’s a chance that something more sinister is lurking beneath the surface.

Bertie would request that Megan didn’t post his face on social media, claiming it was because of his dad’s high-ranking career in the navy (which in hindsight should be the second red flag after the name ‘Lord Bertie Underwood’).
However the fairytale would begin to unravel when Megan noticed letters arriving at their home under various different names. Bertie claimed they were for previous tenants, but the former bar manager was not convinced and decided to investigate further.
What Megan then discovered would bring her world crashing down entirely.
However not everything was as it seemed.
Megan later discovered that Bertie had multiple bank cards under various aliases and after googling the names, she uncovered that her Lord actually had a long track record for fraud, using names such as Robert Doughty and Robert Soanes-Madejski to get away with his crimes.
The truth devastated Megan, who would be dealt another crushing blow once the pair split – with ‘Bertie’ having racked up around £30,000 of debt in her name.
“We went to the police and action fraud,” she recalled to The Sun. “[But] unfortunately there wasn’t a great deal they could do.”

Megan has since worked to pay off the debts and rebuild her life while ‘Bertie’ has since been arrested on fraud charges and sentenced to five years in prison. However he escaped in 2022 and currently remains on the run.
The fact that ‘Bertie’ is now on the run is something which has left Megan unsettled, as she added to Metro that she would ‘freeze’ if she encountered him on the street.
Megan’s story appears as part of the series Love Cheats, which is available to watch on Channel 4.



Leave a Reply