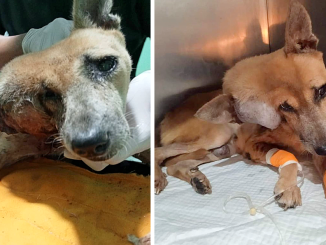
Amidst a beautiful spring scenery, a heart-wrenching tale of a puppy in distress plays out. The poor little pup is separated from his mother and embarks on a challenging emotional journey that explores the universal theme of separation anxiety. The story captures the deep connection that exists between a mother and her offspring, and tugs at the heartstrings.

Puppies rely on their mother not only for food but also for emotional support. Being taken away from their mother can cause distress and feelings of fear, sadness, and vulnerability.
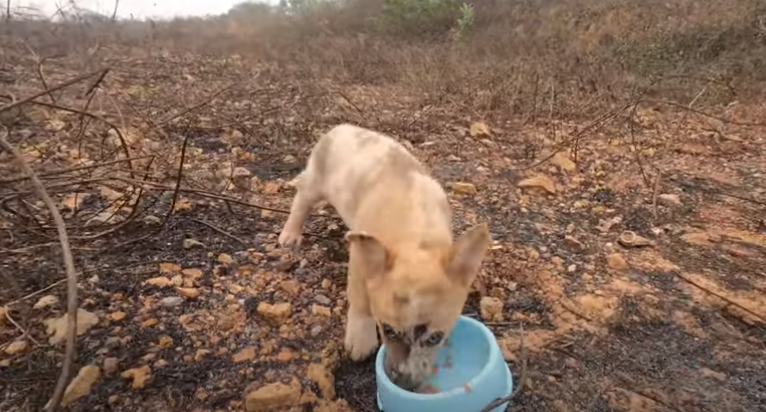

This touching story tells of a puppy who cries out for help, moving those who hear it to feel empathy and kindness. The happy ending highlights the value of reestablishing emotional connections and providing comfort and support. It’s a powerful reminder of how important emotional bonds can be and their lasting impact on a person’s happiness and health.
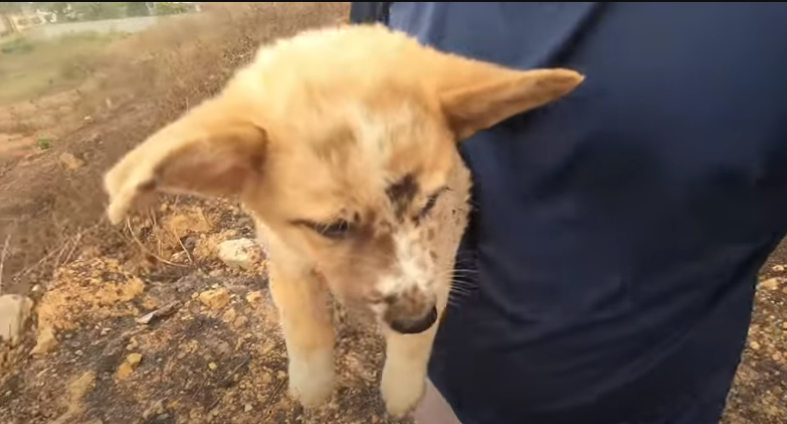

The conclusion of this tale portrays the significance of companionship and the strong emotional connections between animals and humans. The puppy found comfort and encouragement from his mother, highlighting the transformative capabilities of such bonds. This emphasizes the importance of being attentive to the needs of all living beings and offering solace during difficult times, promoting empathy and kindness as essential values.
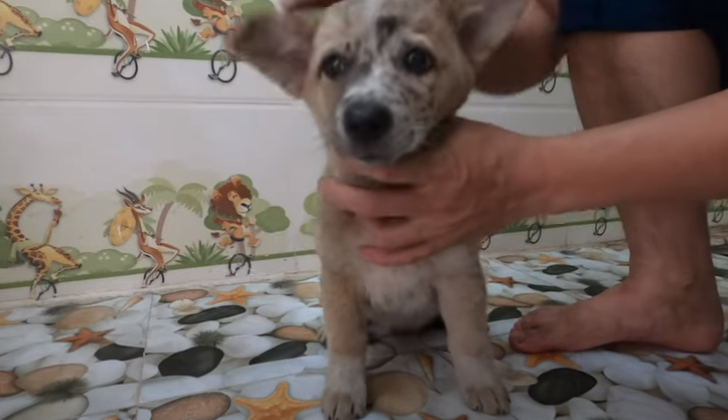

In the end, the tale of the puppy’s cries for aid after being separated from its mother is a heartwarming example of how compassion can be life-changing and how kindness can bridge the emotional divide between humans and animals. It is a reminder that we must pay attention to the needs of all living beings and provide comfort and assistance during times of distress, encouraging empathy and compassion.
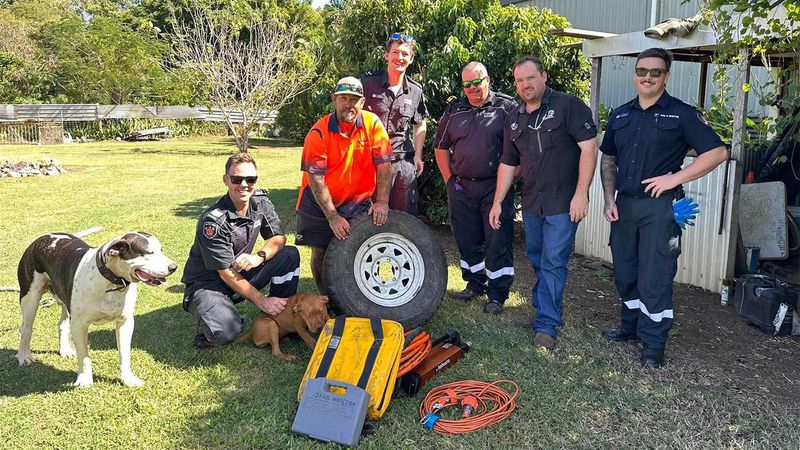
Dog rescued after getting its head stuck in wheel rim
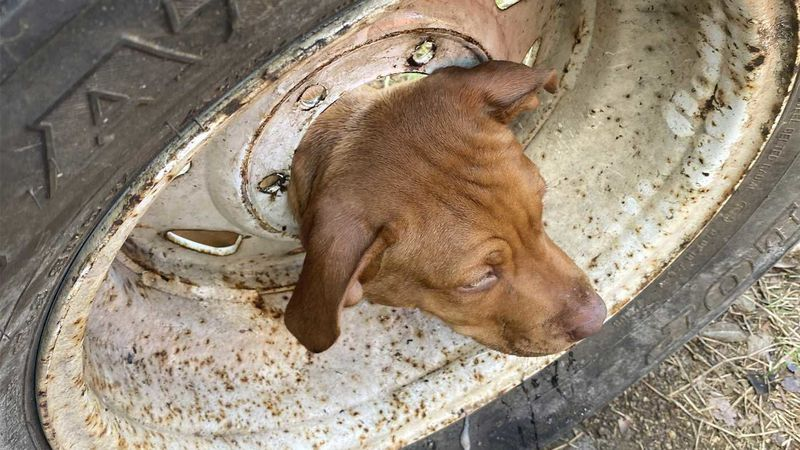

A dog has been rescued from a tight spot by Queensland firefighters armed with a bottle of olive oil and a lot of patience.
The puppy, named Bonnie, stuck its head through the middle of a wheel rim but couldn’t pull itself back out.
It was up to the firefighters at Mareeba Fire and Rescue to figure out a solution to the sticky situation.
“Crews used lots of olive oil and patience to assist in the extrication,” Queensland Fire and Emergency Services said in a Facebook post.
“We hear she’s recovering well.”
Mareeba is a rural town in Far North Queensland, inland from Cairns.



Leave a Reply